List of Diseases
Arthritis the temporomandibular
- inflammatory or inflammatory-dystrophic disease of the temporomandibular joint.

Trauma, including occlusive; General infection-gonorrhea, scarlet fever, measles and local-osteomyelitis of the jaw, mumps, otitis, mastoiditis, etc.
Rest (immobilization with an elastic bandage and a rubber pad between the teeth), heat, salicylates, intra - and periarticular administration of antibiotics and corticosteroid preparations, UHF therapy.

Etiology of temporomandibular arthritis
Trauma, including occlusive; General infection-gonorrhea, scarlet fever, measles and local-osteomyelitis of the jaw, mumps, otitis, mastoiditis, etc.
Pathogenesis of temporomandibular arthritis
Infection is hematogenic-metastatic or contact, inflammation of the joint capsule, then destruction of cartilage and meniscus.Symptoms and course of mastoid-mandibular arthritis
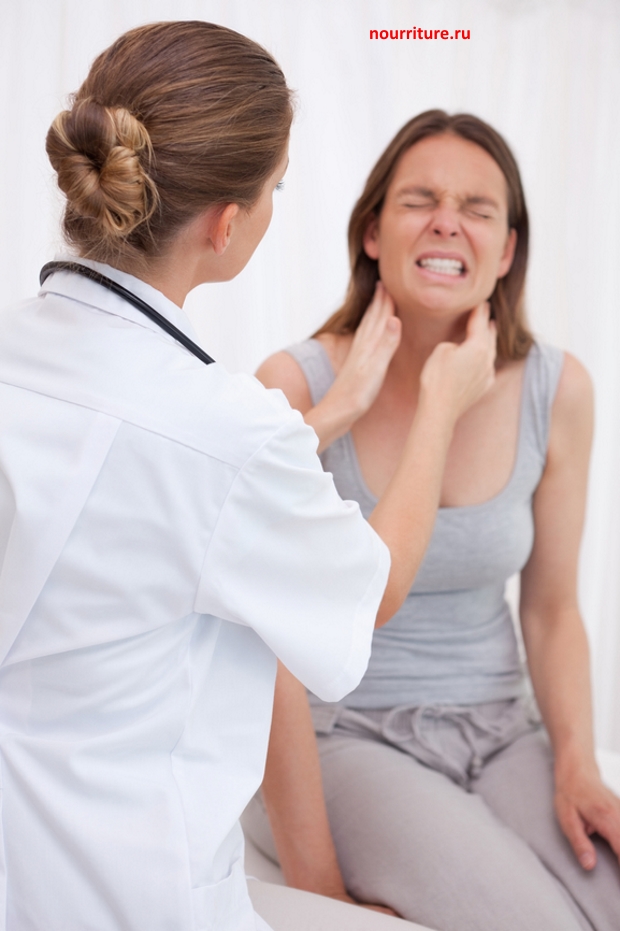
In mild cases-pain that increases with the movements of the jaw, a slight swelling at the tragus of the ear; palpation is painful. With purulent inflammation-a sharp pain that gives to the ear, temple, because of the pain, it is impossible to open the mouth. Body temperature increases, chills are noted, sometimes intoxication. With chronic course of stiffness, clicking in the joint with movements of the jaw, unpleasant sensations. Periodically there are exacerbations.Treatment of mastoid-mandibular arthritis
Rest (immobilization with an elastic bandage and a rubber pad between the teeth), heat, salicylates, intra - and periarticular administration of antibiotics and corticosteroid preparations, UHF therapy.
With the progression of the suppurative process – arthrotomy, with chronic arthritis-physiotherapy (electrophoresis, inductothermy, therapeutic mud), salicylates and orthopedic treatment.
For specific arthritis, appropriate treatment is prescribed. In cases complicated by ankylosis and contracture, treatment is surgical.

