List of Diseases
Periodontitis

- inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues, characterized by progressive destruction of the alveolar process. There are generalized and localized periodontitis.
Generalized periodontitis
Etiology. Soft plaque, occlusal trauma, Tartar, and oral hygiene disorders. It often develops as a complication of chronic forms of gingivitis.
Pathogenesis . It develops as a reaction to soft plaque, in which the inflammatory process spreads from the gums to the underlying tissues; this is facilitated by the weakening of the immune system. Complicated congenital and secondary disease with severe impaired cellular immunity, such as hematologic malignancies, HIV infection, etc.
Symptoms, course. Hyperemia and edema of the gums, the edge of which is usually loosened; damage to the dental groove, the formation of dental pockets; abundant dental deposits. Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, there is a violation of the function of chewing, displacement of the teeth, their pathological mobility, and traumatic articulation.
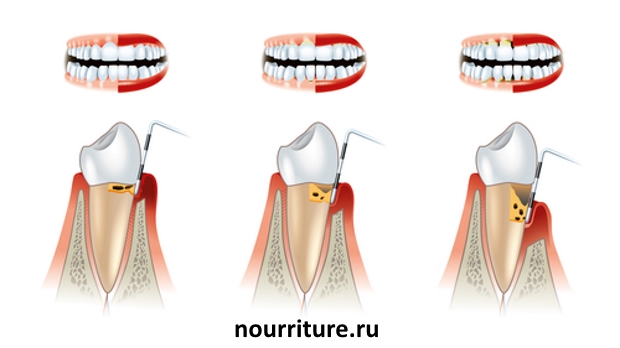
Generalized periodontitis
Etiology. Soft plaque, occlusal trauma, Tartar, and oral hygiene disorders. It often develops as a complication of chronic forms of gingivitis.
Pathogenesis . It develops as a reaction to soft plaque, in which the inflammatory process spreads from the gums to the underlying tissues; this is facilitated by the weakening of the immune system. Complicated congenital and secondary disease with severe impaired cellular immunity, such as hematologic malignancies, HIV infection, etc.
Symptoms, course. Hyperemia and edema of the gums, the edge of which is usually loosened; damage to the dental groove, the formation of dental pockets; abundant dental deposits. Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, there is a violation of the function of chewing, displacement of the teeth, their pathological mobility, and traumatic articulation.
The destruction of the interdental septum is determined radiographically without affecting the base of the alveolar process and the body of the jaws: the contours of the interdental septum are indistinct. Periodic exacerbations are accompanied by the formation of periodontal abscesses with pronounced General disorders (fever, malaise, leukocytosis, increased ESR).

Treatment is complex, necessarily including curettage; surgical, less often non-operative, elimination of dental pockets. In acute exacerbation period and the broad – spectrum antibiotics; the chronic course of the metronidazole. Immunomodulatory drugs. General strengthening therapy. Splinting of teeth and rational dental prosthetics. Prishlifovyvanie bumps of crowns of teeth. Systematic oral care using therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and soft plaque-removing effects. Dispensary observation.
Forecast . Rational treatment and systematic hygienic care of the oral cavity can achieve remission. In the absence of treatment or neglect of the rehabilitation regime-complete destruction of the bone periodontal and loss of teeth.
Localized periodontitis
Etiology: violation of the contact point for approximal caries, injury to the overhanging edge of the filling, details of dentures.
Pathogenesis is associated with damage to the dentoalveolar junction and the formation of dentoalveolar pockets.
Symptoms, course. Stuck food; in acute course and exacerbation of the process-pain, which increases with food, swelling and hyperemia of the gums, abscessing, pathological mobility of the tooth (teeth). With a chronic course –a feeling of awkwardness, food sticking, the gums are thickened, sometimes thinned. On the tooth or adjacent teeth, there are approximal defects, incomplete fillings or artificial crowns.
Forecast . Rational treatment and systematic hygienic care of the oral cavity can achieve remission. In the absence of treatment or neglect of the rehabilitation regime-complete destruction of the bone periodontal and loss of teeth.
Localized periodontitis
Etiology: violation of the contact point for approximal caries, injury to the overhanging edge of the filling, details of dentures.
Pathogenesis is associated with damage to the dentoalveolar junction and the formation of dentoalveolar pockets.
Symptoms, course. Stuck food; in acute course and exacerbation of the process-pain, which increases with food, swelling and hyperemia of the gums, abscessing, pathological mobility of the tooth (teeth). With a chronic course –a feeling of awkwardness, food sticking, the gums are thickened, sometimes thinned. On the tooth or adjacent teeth, there are approximal defects, incomplete fillings or artificial crowns.
Radiographically-resorption of the interdental and intercortical partitions, expressed in various degrees.
Treatment.Removal of the periodontal pockets. With an abscess-opening, with significant destruction of the well-tooth extraction. It is necessary to restore the contact point between the teeth by filling or tabs.
Forecast . Elimination of the periodontal pocket and factors that damage the gingival margin leads to a cure.
Treatment.Removal of the periodontal pockets. With an abscess-opening, with significant destruction of the well-tooth extraction. It is necessary to restore the contact point between the teeth by filling or tabs.
Forecast . Elimination of the periodontal pocket and factors that damage the gingival margin leads to a cure.
